What is Economic Growth and Economic Development
The economics of growth and development are two fundamental concepts in economics. Economic growth refers to the increase in a nation’s output of goods and services, typically measured through Gross Domestic Product (GDP). Economic development emphasises improvements in living standards, healthcare, and education. This article analyses these differences, explores their implications using real-world examples and discusses the role of government policies in promoting both growth and development for sustainable economic progress.
Measuring Progress: GDP vs Human Development Index
The economics of growth and development are two of the most important concepts in economic studies, especially for scholars wishing to grasp their policy implications and sustainable advancement. Although both are related, they have different scopes, measurements, and contributions. Economic growth is the expansion of a country’s production of goods and services, mostly through Gross Domestic Product (GDP), while economic development refers to overall advancements in living conditions, health, education, and well-being.
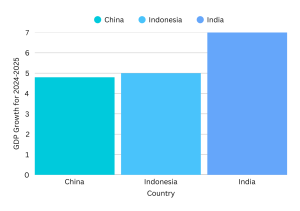
For example, India’s GDP growth rate was recorded at 7.2% in FY24, highlighting robust economic growth. However, disparities in income distribution, healthcare access, and education quality indicate gaps in economic development. Understanding the difference between economic development and economic growth is essential for students aspiring to shape economic policies or conduct research in development economics.
Economic Growth: What The Numbers Tell?
Economic growth refers to an increase in the production of goods and services within an economy over a specific period. It is a quantitative measure that primarily focuses on GDP and per capita income.
Key Features of Economic Growth
- Quantitative Measurement: Growth is assessed using indicators such as GDP, Gross Value Added (GVA), and per capita income. For instance, India’s nominal GDP stood at ₹300 lakh crore in FY24.
- Short-Term Perspective: Economic growth is often driven by short-term policy decisions that may not account for long-term sustainability.
- Sectoral Contributions: India’s economic growth has been driven by sectors like manufacturing and services, supported by government initiatives such as the Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme.
India’s real GDP growth rate for FY25 is projected at 6.4%, driven by stable consumption and investment demand. However, while GDP growth signifies economic expansion, it does not necessarily indicate equitable wealth distribution or improvements in quality of life.
Economic Development: What Defines a Nation’s Success?
Economic development is a broader concept that includes improvements in human capital, income distribution, infrastructure, healthcare, and education. It considers the long-term sustainability of growth and its impact on societal well-being.
Key Features of Economic Development
- Qualitative Improvement: Development is measured using indicators such as the Human Development Index (HDI), literacy rates, and healthcare accessibility. India’s HDI in 2020 stood at 0.645, indicating moderate human development.
- Long-Term Perspective: Unlike economic growth, development focuses on long-term structural changes that enhance the standard of living.
- Holistic Approach: Economic development incorporates social, environmental, and economic factors to ensure inclusive progress.
India has implemented various policies to promote economic development, such as the Pradhan Mantri GatiShakti National Master Plan, which aims to enhance infrastructure and regional connectivity. Additionally, schemes like the National Health Mission have improved healthcare accessibility in rural areas.
Difference Between Economic Development And Economic Growth
|
Aspect |
Economic Growth |
Economic Development |
|
Definition |
Increase in goods/services (GDP) |
Improvement in quality of life |
|
Measurement Indicators |
GDP, GVA, per capita income |
HDI, literacy rates, healthcare access |
|
Focus |
Short-term expansion | Long-term sustainability |
|
Scope |
Macro-level output |
Micro-level welfare improvements |
| Equity | Does not ensure wealth distribution |
Aims to reduce income inequality |
The Role of Government: Growth-First or Development-First?
To balance economic growth with development, the Indian government has introduced various initiatives:
- Make in India: This initiative aims to enhance manufacturing output, boosting GDP growth.
- Startup India: This encourages entrepreneurship and job creation.
- Pradhan Mantri Gharib Kalyan Anna Yojana: The scheme ensures food security for 80 crore citizens until December 2028.
- National Health Mission: This aspect focuses on improving healthcare services in rural areas.
These policies highlight the government’s commitment to achieving both quantitative economic growth and qualitative development.
What Economics Students Must Know About Growth & Development
For students studying economics and public policy, understanding the distinction between economic growth and development is very important.
- Economic Growth Analysis: This enables students to evaluate macroeconomic trends such as GDP expansion and sectoral contributions.
- Economic Development Insights: These help in assessing policies related to poverty alleviation, healthcare, and education.
- Career Relevance: Knowledge of both concepts is essential for careers in policymaking, research, and economic consulting.
Hidden Figures: The Economic Numbers That Matter Beyond GDP
India is progressing in terms of numbers, but does that mean the people are benefitting? A keen insight into the actual facts:
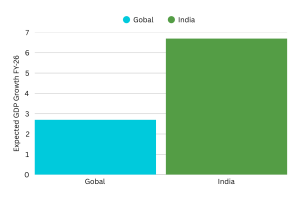
- India’s GDP is projected to grow at 6.7% in FY26, surpassing the global average of 2.7%.
- The richest 10% of Indians own over 77% of the nation’s wealth, highlighting persistent income inequality.
How Jindal School of Government & Public Policy Can Add Value to Your Education
The Jindal School of Government & Public Policy (JSGP) provides a multidisciplinary education in economics, combining perspectives from political science, sociology, and law. Emphasizing quantitative competencies, policy analysis, and data-driven decision-making, JSGP prepares students with the skills to tackle actual economic issues. The university offers research exposure, international networking through international associations, and access to seasoned faculty. Hands-on training, business partnerships, and critical thinking equip graduates for high-value careers in policymaking, consulting, and academia, where they can make a difference in the competitive realm of economics.
Conclusion
Economic growth and economic development, while interrelated, serve different purposes in assessing a nation’s progress. Growth measures the increase in production and income, whereas development ensures improvements in social welfare and sustainability. India’s rapid GDP growth is commendable, but challenges such as inequality and lack of universal healthcare indicate the need for balanced economic development.
For students aspiring to work in economics, policymaking, or research, a clear understanding of these concepts is crucial.
FAQs
- What makes the economics programme at JSGP different from other universities?
JSGP offers an interdisciplinary approach, integrating economics with political science, law, and sociology. The programme also emphasises data science, policy research, and global perspectives, providing a well-rounded education. - Do students have opportunities for research and internships?
Yes, students engage in research projects with faculty, work on real-world policy problems, and have access to internships through JSGP’s strong industry and policy networks. - Is a background in mathematics necessary to apply for the programme?
While having studied mathematics in high school is preferred, it is not mandatory. The programme includes foundational courses in mathematical methods and statistics to help students develop the necessary skills. - What career opportunities are available after completing this programme?
Graduates can pursue careers in government agencies, international organisations, consulting firms, think tanks, and research institutions, as well as advanced studies in economics, public policy, and management. - Does the programme offer global exposure?
Yes, JSGP has partnerships with international institutions, enabling student exchange programmes, research collaborations, and networking opportunities with global policymakers and economists.
References
[1] Ministry of Finance, Government of India. (2024). The Indian Economy – A Review. Available here.
[2] PIB India. (2025). Economic Survey of India. Available here.
[3] Prepp.in. (2024). Economic Growth vs Economic Development: Indian Economy Notes. Available here.
[4] IPPR. (2023). Economic Growth and Development: A Policy Perspective. Available here.
[5] India Budget. (2024). Economic Survey – Chapter 1. Available here.



