Animal welfare and it’s impact on Sustainable Development
July 16, 2024 2024-10-15 6:00Animal welfare and it’s impact on Sustainable Development
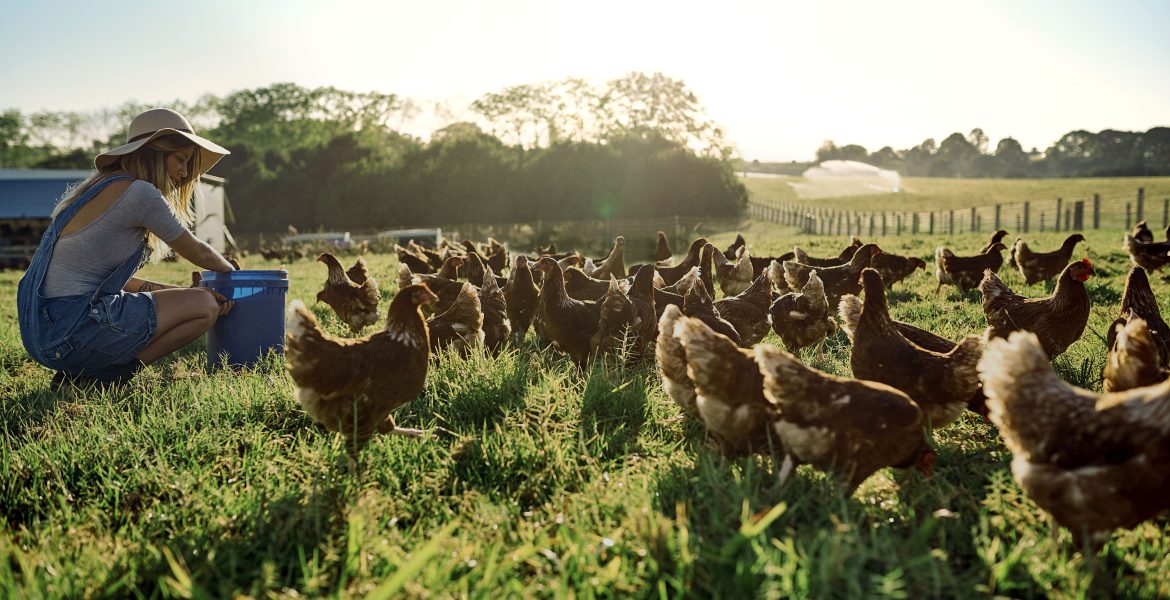

Animal welfare and it’s impact on Sustainable Development
Author: Samridhi Diwan.
The intricate tapestry of sustainability is intricately woven with the threads of animal welfare, creating a seamless bond between the well-being of animals and the long-term viability of our planet. This connection transcends mere environmental concerns and delves into the moral fabric of our society, calling upon us to recognize the profound significance of caring for the creatures that share our world. The sustainable development goals through SDG 12 and SDG 14 support the argument of such interconnectedness between sustainability and animal welfare. Animals, with their diverse behaviours and roles within ecosystems, hold the key to maintaining a delicate balance in the natural world. From the humble pollinators that bring life to flowers to the predators that regulate prey populations, every animal plays a vital part in sustaining the intricate web of life.
The significance of animal welfare in ensuring a long-term sustainable environment and development cannot be overstated. It is imperative that we acknowledge the intrinsic value of animals and make their welfare a priority. Our treatment of animals goes beyond mere utilitarianism; it reflects our values, compassion, and ethical responsibility towards all sentient beings. By nurturing empathy and care for animals, we not only enhance our own well-being but also contribute to the creation of a more compassionate and sustainable society. Recognizing and valuing animal welfare demonstrates our commitment to social justice, environmental sustainability, and the overall health of our planet.
However, the repercussions of disregarding animal welfare are grave and far-reaching, with detrimental consequences for environmental sustainability. The industrial agriculture sector is a prime example of how profit-driven practices often take precedence over the well-being of animals. In pursuit of production efficiency, animals are confined to overcrowded and unsanitary conditions in factory farms. These confined animal feeding operations (CAFOs) not only contribute to the spread of diseases but also result in waste pollution and the depletion of precious natural resources. Similarly, overfishing and destructive fishing practices wreak havoc on marine life, disrupting delicate marine ecosystems and depleting fish stocks, thus endangering the health and balance of our oceans.
Conversely, prioritizing animal welfare brings forth a multitude of benefits for environmental sustainability and development. By championing animal welfare, we actively contribute to the preservation of biodiversity. Safeguarding the habitats and well-being of diverse animal species ensures the delicate balance of ecosystems and secures their long-term viability. Moreover, the ethical treatment of animals translates into reduced environmental impact across various industries. The transition towards more humane and sustainable agricultural practices mitigates pollution, curtails greenhouse gas emissions, and conserves valuable resources, thereby promoting a more sustainable and efficient food system.
Animal welfare should not be viewed as a separate entity from environmental sustainability; rather, it is an integral part thereof. Animals play a pivotal role in ecosystem functioning, contributing to crucial processes such as pollination, seed dispersal, and nutrient cycling. The well-being of animals directly affects the health and resilience of ecosystems. Animals, in their diverse forms and functions, are integral to the delicate balance and rich biodiversity of our ecosystems. They play critical roles in maintaining ecological equilibrium and performing vital ecological services. From the industrious bees diligently pollinating flowers to the majestic predators regulating prey populations, animals contribute to the intricate web of life that sustains our planet. Consider the remarkable phenomenon of pollination, where animals such as bees, butterflies, and birds transfer pollen from one flower to another, facilitating the reproduction of plants. This process is fundamental to the production of fruits, vegetables, and seeds, upon which countless species, including humans, rely for sustenance. However, when animals’ welfare is compromised due to factors like habitat loss, pesticide use, or climate change, their populations decline, jeopardizing the essential process of pollination. This disruption can have far-reaching consequences, causing a decline in plant diversity, reduced crop yields, and a ripple effect throughout the entire ecosystem. Animals also contribute significantly to seed dispersal, aiding the propagation and regeneration of plant species. Through their movements and consumption of fruits, animals transport seeds to new locations, allowing for the colonization of different habitats and the expansion of plant communities. This process is crucial for maintaining genetic diversity, facilitating adaptation to changing environmental conditions and ensuring the long-term resilience of ecosystems. However, when animals’ welfare is disregarded, their ability to fulfil this ecological role diminishes, leading to a decline in plant diversity and a loss of genetic resources.
Additionally, animals play a vital role in nutrient cycling, a process through which organic matter is broken down and transformed into essential nutrients that nourish plants and support the entire food web. From decomposers like fungi and insects that break down dead organic matter to scavengers and detritivores that consume carrion, animals play a crucial part in recycling nutrients and returning them to the ecosystem. When animal welfare is compromised, this delicate balance is disrupted, leading to a buildup of organic waste, nutrient imbalances, and degradation of ecosystem health.
Protecting animal welfare is closely intertwined with conservation efforts and the preservation of natural habitats. Many animal species are intricately linked to specific ecosystems and habitats, relying on them for shelter, food, and reproduction. By ensuring the welfare of animals, we indirectly protect and restore their habitats, creating safe havens where they can thrive. Effective conservation measures involve addressing various threats to animal welfare and habitat preservation. Habitat destruction, driven by activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and intensive agriculture, poses a significant challenge to both animals and their ecosystems. By preserving and restoring natural habitats, we provide refuge for animals, allowing them to carry out their ecological roles and maintain biodiversity. Protected areas, national parks, and wildlife reserves serve as crucial sanctuaries, safeguarding vulnerable species and their habitats. Moreover, combating issues like poaching and illegal wildlife trade is vital for animal welfare and conservation. These activities drive the decline of numerous species, pushing them closer to extinction.
Furthermore, animal welfare holds broader implications for the well-being of the entire world. Achieving sustainability requires adopting a holistic approach that recognizes the interconnectedness of all living beings. In our quest to address the urgent issue of climate change, we must recognize the pivotal role that animal welfare plays in our efforts to mitigate its devastating impacts. It is imperative that we transcend the confines of conventional thinking and embrace a more compassionate and sustainable approach. The industrial-scale production of livestock, a primary contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, cannot be ignored. The current practices of animal agriculture perpetuate environmental degradation and exacerbate climate change. However, there is a glimmer of hope. By transitioning to more humane and sustainable agricultural practices, such as regenerative farming and agroforestry, we can significantly reduce the environmental footprint of animal agriculture.
These innovative approaches prioritize the welfare of animals and promote their natural behaviours, contributing to their overall health and well-being. In turn, this reduces disease transmission, minimizes the need for harmful chemicals and antibiotics, and enhances the resilience of the entire agricultural system. By embracing such practices, we not only protect the welfare of animals but also make meaningful strides in mitigating climate change and fostering environmental sustainability.
Yet, the significance of animal welfare extends beyond practical considerations. It is rooted in profound ethical considerations that speak to our humanity and moral responsibility. Animals, sentient beings capable of experiencing pain, suffering, and joy, deserve to be treated with compassion and respect. When we prioritize animal welfare, we acknowledge the inherent value and dignity of every living creature. Treating animals with compassion and respect cultivates a sense of empathy and responsibility that extends to other environmental concerns. This mindset fosters a culture of sustainability, encouraging practices that minimize harm to the environment, promote conservation, and reduce the exploitation of natural resources.
It becomes our ethical imperative to alleviate unnecessary suffering and foster a world where all beings can thrive. This ethical perspective aligns seamlessly with the principles of environmental sustainability. Both frameworks share a common thread – the responsible stewardship of our planet and its inhabitants. By promoting animal welfare, we embrace a holistic approach to sustainability that recognizes the interconnectedness of all life forms. It compels us to view the world through a lens of empathy and interconnectedness, where the well-being of animals and the health of the environment are inseparable. Ultimately, by prioritizing animal welfare, we contribute to the well-being of the entire world, fostering a harmonious and sustainable relationship between humans, animals, and the environment.
In conclusion, animal welfare is of paramount importance for long-term environmental sustainability and development. By recognizing the connection between humans and animals, considering the dire consequences of neglecting animal welfare, and embracing the benefits of prioritizing animal welfare, we can forge a path towards a more sustainable future. Animal Welfare stands as a vital pillar of sustainability, weaving together the threads of ecosystem balance, biodiversity conservation, sustainable resource use, climate change mitigation, and ethical considerations. By recognizing the profound connection between animal welfare and sustainability, we chart a course towards a future where the well-being of animals and the preservation of our planet are mutually intertwined. Animal welfare is an indispensable component of environmental sustainability, it safeguards biodiversity, reduces environmental impact, and nurtures empathy and responsibility. By championing animal welfare, we take significant strides towards securing the well-being of the entire world and paving the way for a future characterized by sustainability and compassion.