National Logistics Policy 2022
March 20, 2025 2025-03-27 4:50National Logistics Policy 2022

National Logistics Policy 2022
By Animesh Choudhury Sanyal
Executive Summary
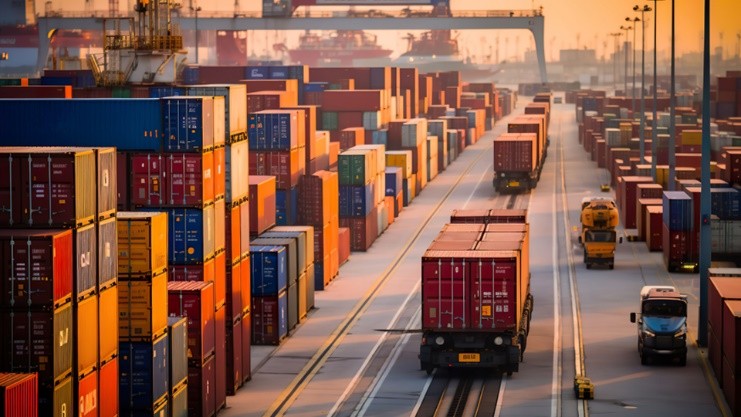
The National Logistics Policy seeks to transform the logistics sector of the country by decreasing cost and increasing efficiency. The major initiatives include integration of Technology thereby digitizing the whole process, creation of multimodal logistics park and improvement of the infrastructure for railways and waterways. This policy aims to make India a global manufacturing hub.
Background
The logistics cost in India accounted for 13-14% of the economy which became a push factor for global businesses and it further elongated the country’s dream to become a manufacturing hub. Therefore, National Logistics Policy was launched on 17th September 2022, in order to reduce the Logistics cost of India to 8-9% of GDP that is equivalent to the global standards which will result in India becoming a feasible option for global businesses who are increasingly opting for China Plus one Policy.This Policy will lead to the establishment of 35 multimodal hubs which will streamline the freight movement process. Moreover, it will also increase the warehousing capacity and facilitate a faster communication to ensure that the products are in a closer vicinity to the consumption points.
Features
Integration of Digital System(IDS) simplifies the coordination amongst various ministries. Moreover, Unified Logistics Interface Platform (ULIP) is devised through this policy which is an unified portal which helps the exporters oversee their consignments by incorporating digital services pertaining to logistics which includes benchmarking services, container tracking and monthly performance analytics. Additionally, the E-logistics Services (E-logs) portal has been setup in order to ensure a speedy resolution of the grievances pertaining to the agencies of the government. The NLP compliments the PM Gati Shakti National Master Plan and together these polices raised the standards of Indian logistics such that India ranked 38 out of 139 in the World Bank Logistics Index showcasing a 6 position rise in comparison to the 2018.
Issues
Despite the transformational success NLP has brought within India’s logistics sector there are still many problems that are needed to be unclogged. Even upto this date the reliance on road transportation for carrying freight from one point to another is largely prevalent despite the high costs of logistics associated with it.It is noteworthy that roadways hold a significant share of 66% of cargo in ton kilometers. Moreover, Railways and Waterways are preferred less in comparison to the roadways mainly because of the inefficient infrastructure developments within these two modes of transportation. Moreover, due to digitization of the entire process, providing uniform internet access to all is a challenge provided the unskilled workers including truckers have to be made digitally literate to access internet while travelling. Moreover, the political tussle between the state government and the central government can create hindrances within this policy as coordination is a key for this policy to be a success.
Recommendations
A system needs to be created which increases the usage of railways as despite being the cheapest mode of transportation for freights it is less prevalent where last mile connectivity should be given the priority in addition to a faster pace of transportation which is possible when separate lines for goods trains are built. Additionally, the cost of financing projects related to logistics are worrisome for the people involved in this sector because of the inconsistency in freight transportation making investments riskier for the lenders. Thus, creation of ancillary options which helps to obtain financing at reduced rates would be beneficial for the success of this policy. Similarly, it becomes easier for the small players to comply with this policy if a norm is added where they are exempted from Goods and Services Tax. Lastly, making sure that there are statutory provisions related to the components of National Logistics Policy would act as a checks and balances on the operationalization of the outlined procedures.
References
Invest India. (2019). Investindia.gov.in. https://www.investindia.gov.in/team-india-blogs/national-logistics-policy-india
Bureau, E. (2023, April 21). India raises its logistics game, rises six spots on World Bank Index to 38. The Economic Times; Economic Times. https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/industry/transportation/shipping-/-transport/india-raises-its-logistics-game-rises-6-spots-on-world-bank-index-to-38/articleshow/99676267.cms?from=mdr
IBEF. (2024). Transforming India’s Logistics Sector: Challenges and Opportunities. India Brand Equity Foundation; IBEF. https://www.ibef.org/research/case-study/transforming-india-s-logistics-sector-challenges-and-opportunities
Global, EY. (2024). Transforming the future of Indian logistics sector. Ey.com. https://www.ey.com/en_in/insights/consulting/transforming-the-future-of-indian-logistics-sector
shetty, sushant. (2022, September 22). Insights on the National Logistics Policy, 2022 – Fox Mandal. Fox Mandal. https://www.foxmandal.in/insights-on-the-national-logistics-policy-2022/